The Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is a disorder of the brain that is caused by prions. This changes the protein structure of the brain, which subsequently changes to a kind of holey sponge. The signs of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease are often similar to those of dementia. Unfortunately, this disease is still incurable, although medicine is doing intensive research in this area.
What is Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease?
What is Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease? The neurologist H.-G. Creutzfeldt was the first to report on Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Shortly afterwards, Alfons Maria Jakob published about the disease. That is why the disease was given the name Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in 1922. It is an extremely rare but fatal disease in humans.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is triggered by proteins (so-called prion proteins) that are misfolded. The particularly dangerous thing about these prion proteins is that the infectious proteins force their changed form on the healthy. Over time, this riddles the brain like a sponge. Therefore the disease belongs to the group of transmissible spongionic encephalopathies (TSE). This means something like: communicable spongy brain disease.
Causes
There are several types of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. If it occurs without an apparent external cause, it is a sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Mostly people over 65 years of age are affected by this. It is the most common form of the disease, but the number of cases has remained relatively constant around the world for years.
The disease can also be hereditary. One then speaks of a hereditary Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. In addition, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease can be triggered by an infection. In particular, the injection of human growth hormones was a clear risk factor. But also the transplantation of human meninges or corneas could trigger an “acquired” Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Another variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD for short) mainly affects people under 30 years of age. It corresponds to the brain disease BSE observed in cattle. The vCJD was first described in England in 1996. VCJD is most likely causally related to the disease known as mad cow disease.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is associated with very serious complaints that significantly limit and reduce the patient’s quality of life. Those affected usually suffer from memory disorders, leading to memory lapses and, in general, confusion on the part of the person concerned.
Often times, patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease also suffer from disorders of orientation or coordination and can easily injure themselves or no longer find their own home. Concentration disorders also occur, so that normal thinking, acting and speaking to other people is no longer possible. It can also lead to paralysis of the entire body, resulting in restricted mobility.
Many patients are dependent on outside help in their everyday life due to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and can no longer cope with everyday life on their own. Furthermore, it can lead to depression or anxiety, with the person affected often trembling or appearing restless. Also, muscle twitching possibility of this disease occur.
The symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of typical dementia. In severe cases, the restrictions can be so great that those affected have to rely on a wheelchair. Recognizing your own family members or other people you know is also difficult. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease ultimately leads to the death of the person affected.
Course
What is the course of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease? In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the patient gradually loses his mental and motor skills at first, but then more and more quickly. In addition to disturbances of perception, painful misperceptions and depression, memory disorders and even dementia occur.
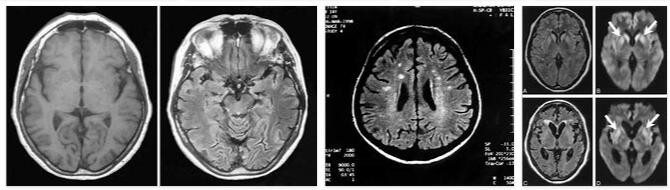
In addition, the coordination of movement sequences is disturbed. In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, muscle twitching and other involuntary movements also occur. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect changes in certain areas of the brain in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
In the late stages of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, a severe drive disorder occurs. In the waking state, the affected person lacks any motivation to move or speak.
According to current knowledge, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease leads to death with an average duration of four to six months. However, there are patients who died after just three weeks and others who were diagnosed with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease after two years.
Complications
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease cannot be treated. The patient suffers from a number of symptoms, which worsen as the disease progresses. Movement disorders and balance disorders occur. It starts with difficulty walking and performing everyday activities such as drinking or holding and using a knife and fork while eating.
At a certain stage of the disease, the patient needs a wheelchair or later becomes bedridden. The muscles also become stiff, so that the patient also needs to be helped with food at a later stage of the disease. There are also psychological difficulties. Personality changes can occur.
The patient needs regular care from trained staff, but also from family members. The family needs a lot of time, patience, and care to care for a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. There is also progressive dementia in the patient. This manifests itself in the deterioration of the ability to concentrate as well as a disturbance of the short-term memory.
Patients become confused and may not recognize their own family members, or only sometimes. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease ultimately leads to the death of the affected patient. This can happen anywhere from a year to a year and a half after the onset of the disease.
When should you go to the doctor?
In Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the protein structure of the brain changes, which ultimately mutates into a kind of holey sponge. Although the disorder is considered incurable, if Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is suspected, the doctor should be consulted immediately so that at least the symptoms can be treated.
The sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease mainly affects people over 65 years of age. People of this age who observe certain symptoms should therefore consult a doctor as soon as possible. Typical for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease are, for example, memory gaps, balance and orientation disorders, poor concentration, paralysis, tremors, depression and anxiety states without a threat.
The above side effects occur with numerous, also much more harmless, diseases. There is therefore no need to panic, but the symptoms should be used as an opportunity to see a doctor as soon as possible. This is especially true if the disorder has already occurred in the family, since there is also a hereditary form of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
A third variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease occurs predominantly in young people under 30 years of age and is associated with the brain disease BSE observed in cattle. The symptoms are the same as in sporadic and hereditary Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Young people should therefore not simply dismiss such symptoms as a stress reaction, provided they occur regularly, but rather consult a doctor promptly.
Treatment & Therapy
How is Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease treated? There is currently no way to treat Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease can neither be stopped nor stopped. A vaccination is also not in sight.
Therefore, so far only the symptoms can be treated in order to provide relief to the patient. Antidepressants (for depression) or neuroleptics (for restlessness or hallucinations) are used. Anti-epileptic drugs (such as clonazepam, valproic acid) help with muscle twitching.
Therapies for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease are currently being researched at full speed. Anti-prion agents have achieved promising results in animal experiments. In addition, work is feverishly on a treatment that will make it possible to stop the disease. So far, American scientists have already achieved success here. Before the final results are available, however, these therapeutic approaches must first be researched in larger patient groups.
In 2000 a patient was diagnosed with vCJD, first in Germany and then in the USA. This patient then apparently recovered. Since this is excluded according to the current state of science, it was probably a misdiagnosis of vCreutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is different for all three variants. It should be noted that it is fatal in all cases. The suddenly occurring variant of the disease leads to the death of the person affected within six months on average. A family-related variant, on the other hand, can last up to 40 months before death occurs. However, shortened pathways to illness are also possible, leading to death within four months. The new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, on the other hand, allows survival periods of an average of 12-14 months as a prognosis.
In addition, the disease courses differ minimally from one another in the three variants. However, all three lead to the typical loss of motor and cognitive abilities in those affected.
A cure is not in sight due to the still not fully understood mechanism of spongiform encephalopathy. Rather, it can be assumed that the hereditary forms will continue to exist. By eliminating and avoiding all sources of danger (various animals and their components; especially cattle brain), diseases from this spectrum can be contained.
According to current knowledge, the emergence of such an epidemic is unlikely. In addition, the hereditary form is not transferable, which makes it a purely genetic problem.
Aftercare
There are currently no well-founded methods of follow-up care for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Since the disease is fatal, follow-up treatment after therapy can only be carried out symptomatically. In addition, there are still no forms of therapy for this disease that cause a cure. At best, the process is slowed down.
The actual diagnosis of CJD can only be clearly established after death by performing an autopsy. If clonazepam is administered against muscle tremors, the valproic acid level is tested regularly and the dose is adjusted to the current course. Magnetic resonance imaging is recommended to illustrate the course of the disease.
Aftercare primarily affects the nursing staff in hospitals. The prions can be transmitted from person to person, but only in direct contact with open wounds, blood or infectious tissue. Conventional hygiene is sufficient for normal patient contact. Infectious material that accrues during operations must be disposed of properly. In the event of impending contact with a patient’s body fluids, disinfect with sodium hypochlorite or sodium hydroxide.
Special protective measures are recommended for surgical interventions. It is advisable to wear double gloves and protective clothing as well as protective goggles. Surgical instruments are disposed of as C-waste. Prions mainly adhere to metallic surfaces and are extremely resistant to conventional sterilization methods, such as killing germs at standard temperatures, alcohol or UV rays.
You can do that yourself
In the case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, the person affected should focus on the processes that he is able to carry out depending on his or her state of health. Since the disease is progressive, it is important that there is a sufficient exchange of information between the doctor and the patient about the further processes.
On this basis, it makes sense if life events are planned and restructured in good time. Methods or accompanying therapies are helpful for emotional strengthening of the sick person. In addition, in order to maintain general well-being, it is important to deal constructively with the fate of the disease. Close coordination with people from the surrounding area is very helpful. Developments can be discussed together and boundaries can be defined in order to minimize the burden on everyone concerned in the social environment.
A mental flexibility is helpful and positive attitude should maintain the sick. In order to maintain motivation and participation in life, it is beneficial when new hobbies are discovered. These should be lived with optimism and confidence. Expectations towards other people should be minimized and one’s own fear should be openly addressed. The exchange with people with the same diagnosis is often inspiring in order to receive helpful tips and to build up mental stability.