According to eshaoxing, the mole of the bladder is a serious complication in pregnancy. Due to a failure in fertilization, the chorionic villi grow vigorously without a full embryo developing. The pregnancy must be terminated with a minor surgical procedure.
What is a mole?
A malgrowth of the chorionic villi of the female placenta is called a mole. The reason for this disorder is a failure in fertilization. As the surrounding connective tissue melts, the placental villi are transformed into bubbles. The trophoplast is subject to increased growth.
There are two types of moles. A partial mole develops in 90 percent of the cases and a complete mole in 10 percent of the cases. In the complete form, no embryo is formed, while in the partial moles, beginnings of the development of an embryo can be seen. Moles are cell growths in the placental tissue, but they are usually not cancerous.
However, they can invasively grow into the surrounding space. In rare cases, however, a so-called chorionic carcinoma can develop. Phenomenologically, the transition between an invasive mole and a cancerous growth appears to be fluid and has not been described uniformly in the literature.
Root cause
The cause of a mole of bladder lies in defective fertilization. In the complete form, the female chromosome set is completely absent. How female genetic information is lost is not yet fully understood. A seedless egg cell can be fertilized with two sperm or with one sperm that is dividing. It is possible, however, that the female chromosome set is subsequently lost due to an incorrect division of the male chromosome set.
The partial mole of the bladder develops from a triploid fertilized egg cell with a female chromosome set and two male chromosome sets. Here an egg cell is fertilized either with two sperm cells or with a dividing sperm cell.
An embryo cannot develop in the case of a complete molar because the genes of the paternal chromosome set are completely inactivated by imprinting. However, the female homologous set of chromosomes is missing. As a result, only trophoplastic tissue develops. In the case of partial molars, however, embryonic tissue can form in addition to the trophoplastic tissue.
Symptoms, Signs & Ailments
Mole pregnancy initially shows all of the normal signs of pregnancy. However, bleeding can occur from the sixth week of pregnancy. The bleeding can occur later. If the mole is complete, there is usually an early abortion. However, if this does not happen, additional symptoms include nausea, vomiting and dizziness.
The abdomen swells because the placenta grows quickly and the uterus expands. The values of the pregnancy hormone “human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)” rise steeply due to the rapidly growing placenta. However, a partial mole is not that easy to spot. The clinical symptoms are not as noticeable and a possible abortion occurs a little later in the period from the fourth to the sixth month of pregnancy.
diagnosis
To diagnose a mole of the bladder, the value of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is first determined. If, in addition to unusual and severe pregnancy symptoms, the hCG levels rise rapidly, a mole of bladder is suspected. The heavily swelling belly also suggests this finding.
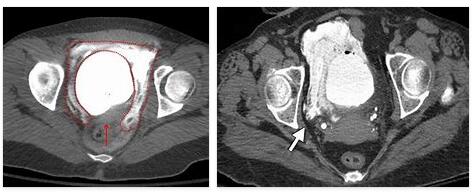
Imaging procedures, such as sonography, can support the examination. Complete moles are usually easily identified by ultrasound scans. However, partial moles are not that easy to diagnose. Nothing can be seen here even during an ultrasound examination.
In this case, it is necessary to carry out cytogenetic analyzes. A tissue sample is taken and genetically examined. If only male chromosome sets are found, a complete mole of the bladder is present. A triploid cell with one female chromosome set and two male chromosome sets has a partial mole of the bladder.
Complications
Various complications can occur as a result of a mole of bladder. First of all, the pregnancy has to be terminated, which is usually associated with emotional and psychological stress for the women concerned. In a third of cases, a mole will develop into cysts on the ovaries.
This can lead to severe abdominal pain, menstrual disorders and indigestion. A rupture of a cyst occurs rather rarely, as a result of which infections and bleeding in the abdomen or a circulatory shock occur. If the cysts twist, a so-called twist of style occurs, which can lead to peritonitis and further complications as a result.
Surgical treatment of a molar mole increases the risk of bleeding and injuries to the cervix. Often, there are also remnants of the mole of the bladder, which can become inflamed years later and require renewed scraping. Even with successful therapy, the chance of becoming pregnant is reduced.
If there are serious complications such as polycystic ovary syndrome, fertility is sometimes permanently impaired. A mole of bladder can lead to long-term menstrual disorders or the complete absence of menstrual bleeding.
When should you go to the doctor?
If you have this complaint, you must definitely consult a doctor. Since the pregnancy is usually terminated due to the abnormal development, a psychologist must be consulted in many cases if the patient and her partner suffer from psychological complaints or depression.
A doctor must be consulted if bleeding occurs despite pregnancy. In most cases, these occur after the sixth week of pregnancy. Persistent dizziness or general malaise can also indicate the disease, so that a doctor examination is necessary.
The expansion and enlargement of the uterus is also a common symptom, so that a visit to a doctor is necessary. In the event of acute pain or emergencies, an emergency doctor should be called or the hospital should be visited. The disease can also be diagnosed by a gynecologist. He can also carry out the corresponding abortion. Successful treatment usually does not result in any particular complications for women.
Treatment & Therapy
A mole of bladder must be surgically removed using a suction curettage once it has been identified. The cervix is widened and the tissue is gently suctioned off. Sometimes a second procedure is necessary because not all of the molar tissue has been captured the first time. In addition, drugs are administered that are supposed to repel the remaining tissue. These drugs come in the form of tablets, gels, or vaginal suppositories.
Even after the treatment, the development of the moles must be monitored for a long time. If individual cells are left behind, they can grow again after a certain period of time. The pregnancy hormone level should be tested for up to six months. Low values indicate the complete removal of the moles.
However, if the values increase again, another operation may be necessary. Because occasionally the mole grows into the uterine muscle. In this case, a suction curettage cannot capture the entire tissue. Signs of this are constant bleeding despite treatment. With the invasive forms of moles, only chemotherapy can bring a complete cure.
Since the tissue is usually not malignant, the chances of recovery are very good. However, in rare cases, malignant chorionic carcinoma develops, which requires more intensive treatment and monitoring. However, even with malignant degeneration of the moles, there are good chances of recovery from chemotherapy.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of a mole of bladder depends on the individual circumstances. If the progression is optimal and there are no further complications, corrective surgery can result in permanent healing.
If the outcome is less favorable, the expectant mother is at risk of an abortion. In very severe cases, permanent infertility of the woman can then occur. Without medical care, an abortion occurs. The pregnant woman usually loses her baby within the first few weeks of pregnancy and also suffers from severe emotional and psychological problems.
Treatment increases the chances of recovery immensely. The changed tissue is carefully removed in one procedure. This procedure requires the highest level of precision and a sure instinct. Complications result in harm to the unborn child or the immediate loss of the child. Regular check-ups are then necessary as the pregnancy progresses. The uterus is checked for possible changes.
In some cases, tissue regrowth and mole relapse occurs. In order to ensure the survival of the child, another intervention is necessary, which is again associated with great challenges and risks for an abortion. If complications and an abortion occur during the procedure, the damage to the uterus can be so immense that infertility occurs.
Prevention
A mole prevention is unfortunately not possible because its development is caused by a failure during fertilization. Another pregnancy is possible again. However, a new pregnancy should not follow immediately after a mole that has been overcome, but only after it has completely healed.
You can do that yourself
Patients with moles usually undergo an operation soon after the diagnosis of the disease, in which the removal of the malformation by means of suction curettage is in the foreground. The operation is usually associated with loss of the embryo and thus termination of the pregnancy. The women affected are therefore confronted with both physical and emotional problems. Self-help measures are partially possible, but only in consultation with the treating team of doctors.
After the operation, the sick treat themselves to physical rest, avoiding sports and excessive exercise. In some cases, an inpatient stay makes sense. Prescribed medication must always be taken on time, with patients paying more attention to possible side effects. A continuous follow-up check is of great relevance, as further malformations occur in rare cases.
Since the termination of pregnancy that is associated with the mole in particular is associated with a high level of psychological stress, patients try to avoid further stress and to rest. If possible, the patients treat themselves to a few days off and support body and psyche in regeneration after the surgical procedure. If the emotional impairment is too great, affected women seek help from a psychotherapist. This reduces the risk of long-term psychological damage and depression.