A bladder rupture or bladder tear is usually caused by strong external force. In most cases, surgical treatment is carried out.
What is a bladder rupture?
According to theinternetfaqs, the bladder rupture (bladder tear) is a tear in the urinary bladder. In most cases, a ruptured bladder is accompanied by pain. Another symptom of a ruptured bladder is red blood cells (seen under a microscope) or small amounts of blood (visible to the naked eye) in the urine.
A rupture of the bladder also often has a bulge above the pubic bone; Such a bulge is caused either by urine or by a hematoma (a bruise). In addition to a strong urge to urinate, a ruptured bladder can also irritate the peritoneum.
In medicine, a distinction is made between the so-called extraperitoneal (outside the abdominal cavity) bladder rupture, the intraperitoneal (inside the abdominal cavity) and the spontaneous rupture. The extraperitoneal bladder rupture occurs most frequently.
Causes
The most common cause of a bladder rupture is fractures (ruptures) of the pelvic ring. Such pelvic fractures are usually the result of strong forces and can occur in traffic accidents or falls from a great height.
Splinters of the pelvic bone can damage the bladder wall after a pelvic fracture and thus cause a rupture of the bladder. Sudden external pressure on the abdomen can also cause a rupture of the bladder. A corresponding pressure can be exerted, for example, by seat belts.
In the rare cases in which a bladder rupture occurs spontaneously, the bladder has usually been exposed to long-term stress in the past. So-called open bladder ruptures are usually the result of gunshot or stab wounds.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
A rupture of the bladder manifests itself primarily as abdominal pain and pain when urinating, which increase in intensity and duration as the disease progresses. The urinary behavior is disturbed and the person concerned urinates more or less often than before (urinary retention).
Nevertheless, there is a constant urge to urinate, which is associated with the characteristic feeling of pressure in the bladder area. As it progresses, a ruptured bladder causes bleeding, which is manifested by blood in the urine. Occasionally, hematomas also form, which in turn can be associated with pain and pressure in the lower abdomen or in the area of the urethra.
If necessary, enters a peritonitis, which with nausea and abdominal pain, loss of appetite and fever associated. Some sufferers from palpitations and dizziness. In addition, there is a general weakness that manifests itself in the form of tiredness, exhaustion and an overall reduced physical and mental performance.
External symptoms of a bladder rupture are paleness, increased sweating and occasionally swelling in the lower abdomen. The doctor can clearly diagnose the injury based on the symptoms and complaints mentioned. An ultrasound examination can reveal other abnormalities such as the rupture itself, but also urinary congestion and internal hematomas.
Diagnosis & course
The suspected diagnosis of bladder rupture is often possible for a treating physician on the basis of the symptoms present and the patient’s description of his or her previous medical history. If a patient’s symptoms occur immediately after an accident, what happened in the accident can provide further evidence of a bladder rupture.
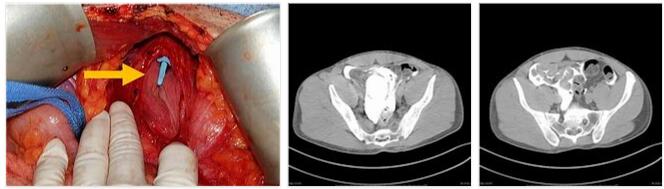
In order to confirm the suspected diagnosis of a bladder rupture, the next step is often a sonography (i.e. an ultrasound examination). With this examination method, the tissue structure of the urinary bladder can be visualized. Computed tomography (CT ; another imaging method) can be used, for example, to rule out injuries accompanying a bladder rupture after serious accidents and / or pelvic fractures.
The course of a bladder rupture varies from person to person and depends on the causes and the earliness of medical treatment. If treatment is started early, a rupture of the bladder has a positive outcome in most cases and the injury to the bladder wall can be healed.
Complications
As always, when illness or organ damage has occurred, further complications must be avoided in the first place. In the case of a rupture of the bladder (rupture of the urinary bladder wall, usually due to external influences), it is no different. This diagnosis can mean that if treatment is delayed or not received, it can lead to inflammation of the peritoneum (peritontitis), a disruption of the intestinal passage (paralytic ileus) or blood poisoning (urosepsis).
These complications can occur because the contents of the bladder empty either intraperitoneally (into the abdominal cavity) or extraperitoneally (into the surrounding tissue). How are the complications noticeable? The complication in the form of peritonitis is noticeable through severe abdominal pain and increasing defensive tension of the entire abdominal muscles up to a board-hard abdominal wall.
Urosepsis without shock can have a lethality (fatal course) of 13 percent, with shock of 28 percent and in a shock situation after sepsis of 43 percent. The complications are therefore by no means to be ignored. Immediate consultation with a specialist (urologist) is urgently recommended so that the complications described here do not occur in the first place or even develop further.
When should you go to the doctor?
A rupture of the bladder is often not recognized because the causes can usually be traced back to other illnesses or accidents. Most often, an injury to the pelvis, particularly a fracture of the pelvic ring, causes a bladder tear because the bladder wall is injured by fragments of bone. Although those affected are always looked after by a doctor in such a situation, it is not uncommon for the doctor to concentrate on the more serious injuries and overlook the ruptured bladder.
Patients should therefore inform themselves of the possibility of a rupture of the bladder if this exists and if symptoms occur that are typical of this type of injury.
The possibility of a bladder rupture is always given when the bladder has been subjected to violence or strong pressure. The risk of injury is particularly great when the organ is bulging with urine. In the event of an emergency stop, the seat belt in the car can trigger a bladder rupture. The attending physician should be made aware of such processes. This is especially true if symptoms such as a strong urge to urinate and painful urination occur. Then, in any case, an ultrasound examination should be carried out to determine whether the bladder has been injured in an accident.
Treatment & Therapy
A suitable therapy for a bladder rupture is dependent on the form of the rupture and also on any accompanying injuries suffered. If a bladder rupture is accompanied by other physical injuries, these also require appropriate treatment.
An intraperitoneal bladder rupture is treated with surgical procedures in most cases. For this purpose, the torn urinary bladder is first exposed in order to be able to sew the tear that has occurred. As a rule, a patient treated in this way is then supplied with an indwelling catheter (a catheter that has to be worn for a long period of time) that runs through the urethra. Such an indwelling catheter after a bladder rupture is used to continuously empty the urinary bladder.
If a patient has an extraperitoneal rupture of the bladder, the extent of the tear usually determines the further medical procedure; In the case of a very minor bladder rupture, it may occasionally be possible to forego surgical procedures and limit therapy to the placement of an indwelling catheter.
If a bladder rupture was caused by a pelvic fracture, this accompanying fracture can be counteracted, for example, with the help of so-called osteosynthesis; This is a surgical procedure that restores the functionality of the injured pelvic bone.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of a bladder rupture depends on the severity of the disease, the earliest possible start of treatment and the patient’s state of health. There are good prospects of recovery as soon as there are no previous illnesses and if the person concerned receives early medical care. The larger the rupture of the bladder, the higher the likelihood of organ failure. In severe cases, blood poisoning or other serious complications can occur. A fatal course of the disease would then be possible.
Without treatment, only a slight rupture of the bladder will heal. The existing self-healing powers could then be sufficient for the patient’s recovery. This step is not recommended as the healing process is significantly longer and there is a risk that the bladder rupture will intensify. In addition, various complications can arise that pose a health risk.
Most patients can be discharged as cured after a few weeks of treatment. In a surgical procedure, a correction is made so that the bladder is then fully functional again. The operation is associated with the usual risks and side effects. Despite healing, a new bladder rupture can occur in the course of life. In order to avoid recurrence, the causes of the occurrence should therefore be clarified and treated.
Prevention
Since accidents and other sudden forces causing a bladder rupture usually occur unexpectedly, the injury can hardly be prevented. A spontaneous rupture of the bladder can be counteracted to a limited extent by seeing a doctor early in the event of symptoms affecting the urinary bladder; this can often prevent long-term health damage to the urinary bladder.
Aftercare
The ruptured bladder is difficult to treat due to the location of the trauma and the wound may open again. Comprehensive aftercare is all the more important. Follow-up care includes regular hospital examinations for the first ten to twelve weeks. These include blood pressure measurements, urine tests and, depending on the situation, imaging controls.
If it is suspected that the kidney function has not been fully restored or that other complications occur, a so-called scintigraphy must also be carried out at intervals, during which the kidney is checked using modern methods. In addition to the medical measures, the person concerned must continue to take it easy.
Physical exertion, especially endurance sports or bodybuilding, must be avoided. Swimming and light exercises from physiotherapy or yoga may be permitted. The patient should discuss with the doctor which individual measures are sensible and do not endanger the bladder.
If there are any unusual symptoms, it is best to inform the attending physician. He can carry out a further examination and, if necessary, arrange another operation. If follow-up care is carried out according to the doctor’s instructions, there are usually no major complications and the rupture heals completely within three to six months.
You can do that yourself
If you have a ruptured bladder, you should definitely see a doctor. In addition to medical treatment, the symptoms of a rupture can be alleviated by various home remedies and tips.
Willow bark tea, an extract from marigolds or a cure with the extracts of the devil’s claw help against the pain when urinating. Typical medicinal herbs and plants such as verbena root, gentian or elderberry, which can also be used in the form of teas or extracts, have also proven themselves.
An irritated bladder can be treated with hot and humid pads. Hot water bottles, cherry stone pillows or a hot shower are just as effective. The latter should be done with a pH-neutral washing lotion or a special intimate washing lotion for bladder diseases.
Increased intimate hygiene is generally recommended in the case of a ruptured bladder. In the case of smaller tears, it may be useful to wear an adult diaper. In addition, low-irritation underwear should be worn to avoid further irritation of the genital area and especially the bladder. In general, other bladder diseases such as bladder or urethritis should be avoided. As a result, and through an early medical evaluation, a severe course and further complications can be prevented in the event of a bladder rupture.