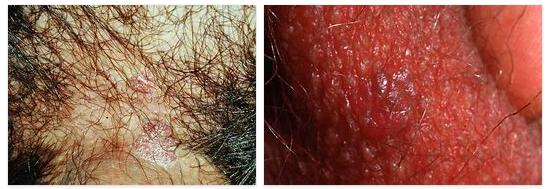
In the bowenoid papulosis is a skin infection caused by human papillomavirus. This leads to papular changes in the skin in the genital region.
What is bowenoid papulosis?
In medicine, the bowenoid papulosis is also known as the condylomata plana. What is meant is a skin infection caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Bowenoid papulosis is characterized by papular skin changes in the genital area.
According to topbbacolleges, bowenoid papulosis is a symptom on the one hand and an infection on the other. In addition, there is a risk of serious consequences from the skin disease. Human papilloma viruses can also cause carcinomas of the anus, penis and uterus. People between the ages of 20 and 40 are particularly affected by Bowenoid papulosis.
Bowenoid papulosis was first described in 1970. In 1978, a subspecies of the disease that affects the region of the scalp and whiskers was also identified.
Causes
Bowenoid papulosis is caused by human papilloma viruses. More precisely, they come from HPV groups 16, 18, 31 and 33. These are sub-forms (serotypes) of certain viruses that are considered high-risk types (high-risk types). These viruses run the risk of causing cancerous growth.
The DNA of these high-risk serotypes can be detected in around 90 percent of all cervical dysplasias. It is therefore assumed that the pathogens also play a role in the pathogenesis of penile cancer and cervical cancer. Bowenoid papulosis is often a reliable indicator of an infection with human papilloma viruses.
A doctor should therefore be consulted as soon as possible if this skin disease is suspected. Bowenoid papulosis is almost always transmitted through skin contact. As a rule, it is unprotected sexual intercourse.
Bowenoid papulosis is also one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. In many cases, however, the infection goes unnoticed. In rare cases, the human papillomavirus can also be transmitted through towels that have been shared.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
A typical feature of Bowenoid papulosis is the appearance of papules with a red-brown color that are flat and velvety. These are the size of the head of a pin or a lens and have a diameter of between two and eight millimeters. The papules, which are sometimes macerated, appear primarily on the glans penis in men and on the large and small labia in women.
However, these changes to the skin do not cause pain. Mild itching is only seen in rare cases. Sometimes the affected people do not even notice the infection because of this. Other patients usually undertake self-therapy.
However, since there is a risk of transition to vulvar or penile cancer, treatment should be carried out by a doctor. The papules often form within a short period of time in bowenoid papulosis. Sometimes, however, their growth also takes place very slowly over the years.
Diagnosis & course
A visit to the doctor is unavoidable if a bowenoid papulosis is suspected. An experienced doctor will notice dyskeratotic cells in the dermis. They are considered to be the early stages of carcinoma in situ. This is an epithelial tumor that does not grow invasively. So it only develops intraepithelially. With this circumstance, the diagnosis of bowenoid papulosis can be confirmed.
Another confirmation is the strong similarity to Bowen’s disease. There is also the option of detecting the DNA of the human papillomavirus using a polymerase chain reaction. Hybridization and sequencing also make it possible to determine the exact viral serotype of the HP virus before the first symptoms appear.
However, if the concentration of the virus is too low, there is a risk of false negative results. The course of the bowenoid papulosis is different. After a few months, spontaneous healing without medical treatment can occur. If the symptoms do not go away, however, there is a risk of carcinoma formation, which in the worst case can even result in the death of the patient.
Complications
In many cases, bowenoid papulosis does not cause any further complications or complaints. Patients recognize papules in the genital area. However, these are not identified in all cases. Many sufferers also take self-help measures to combat the bowenoid papulosis. This is often successful, so that the papules disappear again and there are no further complaints.
In severe cases, the symptom can progress to cancer of the vulva or the penis. Medical treatment is definitely necessary. Bowenoid papulosis rarely causes pain or itching. Medical treatment takes place without complications or discomfort. It is mainly carried out with lasers, with which the upper layers of the skin are removed.
This effectively combats the bowenoid papulosis. There is no pain for the patient. However, there is no guarantee that the bowenoid papulosis will not recur. After the treatment, further examinations are usually carried out to verify the success of the treatment. To prevent further complications, young people should vaccinate against the HP virus.
When should you go to the doctor?
Bowenoid papulosis is an infection with human papillomavirus (HPV). The infection can lead to serious long-term consequences and must be treated promptly by a doctor. Possible complications are carcinomas of the anus, penis or uterus. Since the disease is contagious, a person affected should not only see a doctor themselves, but also motivate their sexual partners to do so.
The incubation period, i.e. the time between infection and the onset of the disease, can be very long and can be several years. It is therefore usually no longer possible to determine from whom a person was originally infected. However, if the carrier is known, the person concerned should be informed about the incident so that they can seek medical treatment.
Patients recognize Bowenoid papulosis by a number of symptoms. In women, these include, above all, pinhead-sized, red-brown colored papules that form predominantly on the inner and outer labia. The skin changes are sometimes, but not always, accompanied by itching. In men, the papules mainly appear on the penis. Anyone who notices these symptoms should not hope that these skin changes will go away on their own, but rather consult a specialist in skin and sexually transmitted diseases immediately. It is best for women to consult their gynecologist.
Treatment & Therapy
Bowenoid papulosis is usually treated by removing the changes in the skin. The doctor uses an electrocautery or a carbon dioxide laser. Electroacoustics is the surgical severing of tissue structures with the help of an intense electrical current.
Another therapy option is the removal of the papules by curettage or diathermy. Diathermy is also known as high-frequency thermal therapy and is one of the electrotherapeutic methods. With the help of electrical current, heat is generated within the body tissue. The infected tissue can be separated and locally destroyed by the high-frequency current.
Due to the strong blood supply to the genital tissue, diathermy is the most sensible therapy method because it causes less bleeding. During curettage, the infected tissue is scraped off. Even after the papules have been successfully removed, regular follow-up examinations must take place because there is still a risk of malignant degeneration.
Outlook & forecast
In general, the prognosis for bowenoid papulosis is favorable. With the available options, the disease can be alleviated and cured. The choice of the therapy path is to be chosen according to the individual preferences of the patient, since good healing results can be achieved with conventional medicine and alternatively.
The self-healing powers of a basically healthy person with a stable immune system are sufficient for recovery. Normally, you will be free of symptoms within a few weeks. For patients with other illnesses or emotional distress, medical care can greatly accelerate the healing process.
A recurrence of bowenoid papulosis cannot be ruled out in principle. The chances of recovery do not change even if the disease occurs again. You are still good. In rare cases, the bowenoid papulosis leads to the formation of a carcinoma. This sequelae can be fatal without timely and comprehensive medical supervision.
It is therefore important that the patient undergoes a check-up and, in the event of irregularities, agrees to treatment as soon as possible. The prognostic outlook with the carcinoma is crucially dependent on the diagnosis and the existing health of the patient. With a weakened immune system, the organism has few resources that would be helpful for cancer therapy.
Prevention
A general vaccination against HP viruses is recommended to prevent bowenoid papulosis. It is considered useful for girls and boys between the ages of 12 and 17. In addition, it is advisable to protect yourself with a condom during sexual intercourse.
Aftercare
With this disease, the person affected usually has very few or no special measures and options for follow-up care available. First and foremost, the disease itself must be treated so that further complications and complaints do not occur. An early diagnosis always has a positive effect on the further course and can also alleviate other complaints.
In most cases, the person affected with this disease is dependent on regular treatment by a doctor, which should permanently alleviate the symptoms. Self-healing cannot occur. After the papules or pustules have been removed, the doctor usually has to carry out a further check.
The affected areas should be wrapped in a bandage so that there are no infections or other diseases. Further follow-up measures are usually not necessary. Since the disease can also lead to a malignant tumor, regular examinations by a doctor are generally very useful in order to detect this tumor at an early stage and continue to remove it. Some people may need psychological treatment for this disease.
You can do that yourself
Patients with Bowenoid papulosis first turn to a health professional to help them recover faster. Usually, the doctor removes the papules using different methods, whereby the patient has to follow certain rules of behavior after the treatment.
Above all, it is important not to undertake any further obligations on the day of the procedure and to refrain from physical activities, especially any kind of sport. The patient must discuss exceptions with the attending physician. Depending on the severity of the surgical procedure, the healing of the bowenoid papulosis is beneficial if the patient allows himself a few days of physical rest and avoids additional emotional stress.
In order to support their own recovery, patients with Bowenoid papulosis pay particular attention to adequate personal hygiene. The doctor informs the person concerned about appropriate hygiene measures in order not to irritate the operated areas and to prevent complications. It is also extremely important that patients with Bowenoid papulosis avoid sexual intercourse.
The treating doctor determines the duration of this abstinence. Regular follow-up checks help to monitor the healing process and, if necessary, to intervene in good time if complications arise. Sports activities are also only to be resumed after the operation after consulting a doctor.